William Butterfield Paintings
William Butterfield was an English architect, renowned for his role in the Gothic revival architecture movement of the 19th century. Born on September 7, 1814, in London, England, Butterfield became one of the most prominent architects of his time, leaving a lasting impact on church architecture in Britain and beyond. His work is characterized by its use of polychrome brickwork, which became a hallmark of his style.
Butterfield's career began after he was articled to a builder in Pimlico, a district of London, where he gained practical experience in the construction industry. This early exposure to the practical aspects of building would serve him well in his later architectural projects. He was deeply influenced by the Oxford Movement, an affiliation that steered his work towards the Gothic revival style, a movement that sought to revive medieval Gothic architectural forms.
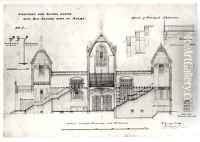
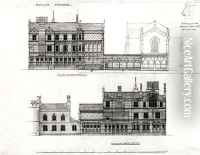
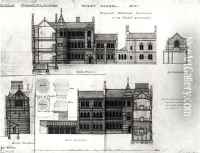
Among his most famous works is the design of Keble College, Oxford, completed in 1876. This project exemplified his innovative use of colored bricks and tiles to create intricate patterns and textures on the building's facade, a technique that was groundbreaking at the time. Other notable projects include St Mary's Church in Dalton Holme, East Yorkshire, and All Saints, Margaret Street in London, which is considered one of his masterpieces. All Saints, in particular, is acclaimed for its rich interior decoration and use of polychromy, embodying the principles of the Gothic revival movement.
Butterfield was not without his critics, some of whom found his use of color and ornamentation excessive. However, his bold approach and dedication to detail earned him the respect of many contemporaries and later architects. He was a meticulous designer who paid great attention to the crafting of small architectural details, from the design of furniture and fittings to the selection of tiles and bricks.
Butterfield's contributions to architecture extended beyond his individual projects. He was influential in promoting the ideals of the Gothic revival, contributing to the wider adoption of this style across England and internationally. His work inspired a generation of architects and designers who sought to blend historical architectural styles with the demands of modernity.
William Butterfield died on February 23, 1900. His legacy is preserved in the numerous churches, colleges, and buildings he designed, which continue to be admired for their architectural beauty and historical significance. Butterfield’s dedication to the Gothic revival and his innovative use of materials and color left an indelible mark on the architectural landscape of the 19th century.