Etienne Duperac Paintings
Etienne Duperac was a prominent French artist, engraver, and architect of the Renaissance period, born in Bordeaux, France, in 1535. His contributions to the arts are significant, particularly in the realm of engraving and illustration. Duperac's work is noted for its detailed representation of contemporary structures and urban landscapes, providing valuable historical insights into the architecture of his time.
Duperac traveled to Italy early in his career, where he was influenced by the Italian Renaissance, a movement characterized by a resurgence of interest in the classical arts and humanist philosophy. The Italian Renaissance left a profound impact on Duperac’s style and choice of subjects. He spent a considerable amount of time in Rome, which was then a hub of artistic innovation, and this experience enriched his perspective and artistic repertoire.
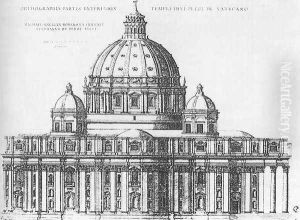
While in Rome, Duperac became involved in various projects, including the Villa d'Este in Tivoli, where he created a series of engravings that depicted the villa’s elaborate gardens and water features. These works were later published and contributed to the spread of the Italian Renaissance garden style throughout Europe. Additionally, Duperac is well-known for his series of engravings titled 'Vestigi dell'antichità di Roma' (1575), which documented the ancient ruins of Rome. This collection was instrumental in disseminating knowledge of Roman antiquities and contributed to the burgeoning interest in archaeology and history that characterized the period.
Duperac was also active in the documentation of contemporary urban development. His most notable work in this regard is the 'Ichnographia', an accurate and detailed plan of Rome published in 1574. It serves as a valuable record of the city’s appearance in the late 16th century and reflects the urbanistic changes that took place during the Renaissance.
After his extensive work and impact on the art scene in Italy, Duperac returned to France, where he continued his career until his death in 1604. His legacy is preserved through his influential engravings and contributions to the understanding of Renaissance architecture and urban planning. Duperac's work remains a subject of study for art historians and provides a visual record of an era that significantly shaped Western art and culture.